By Rahul Pandita
26th Jun, 2024
Source: Statista
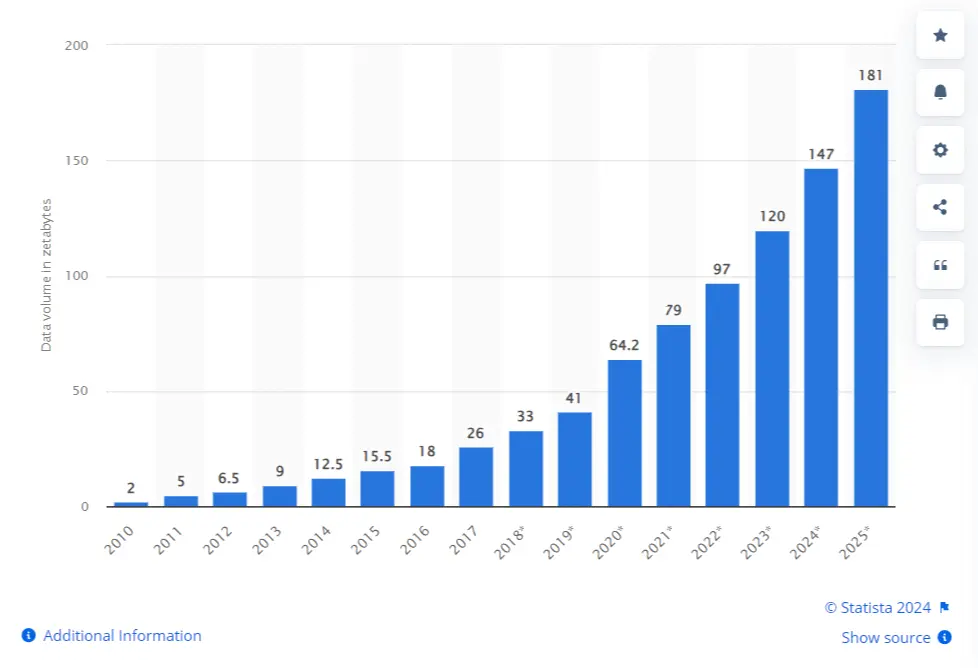
The total amount of data created, captured, copied, and consumed globally reached 64.2 zettabytes in 2020.
64,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 bytes!
By 2025, global data creation is projected to grow to more than 180 zettabytes.
Types of Data an Organization Generates
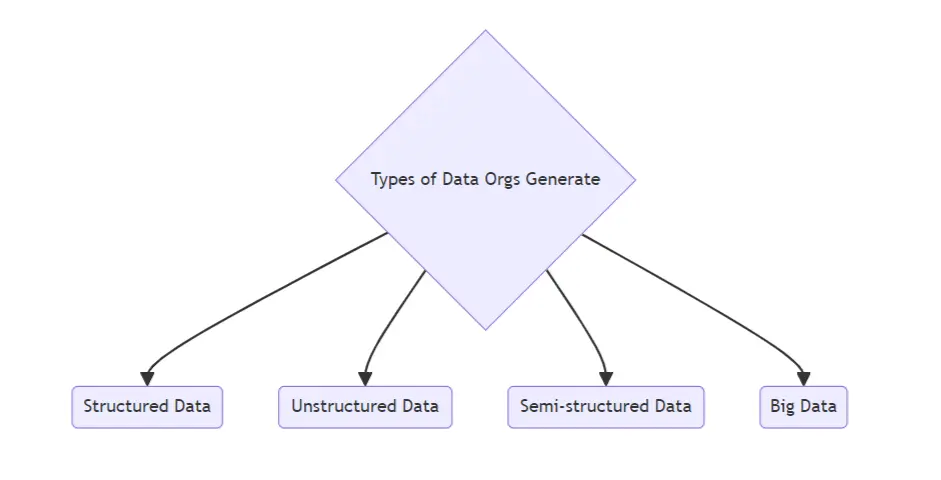
Structured Data
Examples of Structured Data:
- Names
- Dates
- Phone numbers
- Product names or numbers
- Transaction information
Unstructured and Semi-Structured Data
Examples of Unstructured Data:
- Images (human- and machine-generated)
- Video files
- Audio files
- Social media posts
- Product reviews
- Messages sent by SMS or online services
Semi-Structured Data: Some data, such as emails, are considered semi-structured. Email headers contain metadata like the date, language, and recipient’s email address, which are structured. However, the email body, containing the message, is unstructured.
Big Data
Volume: Vast quantities of data put high demands on storage, manipulation, and processing systems.
Variety: The diversity of data types and structures has increased, including emails, images, videos, audio, IoT readings, and scanned documents. This variety can complicate storage, extraction (‘mining’), and analysis.
Velocity: The rapid generation of data poses challenges for analysts, as real-time decision-making becomes crucial for business success.
The Challenge with Unstructured Data and Big Data
While organizations have become adept at managing structured data in databases and spreadsheets, the explosion of unstructured data and big data volumes poses significant challenges.
Unstructured data now makes up around 80% of the typical organization’s data.
However, most companies lack the tools and processes to effectively capture, store, analyze and derive insights from this unstructured information.
- A 2021 survey found that 61% of companies believe the fast-growing volume of data is limiting their ability to fully harness their data.
- Over 80% of IT decision-makers agree their analytics projects are delayed due to data not being available in the required format.
The problem is even more acute with big data – the massive, fast-moving volumes of data from sources like IoT sensors, web clickstreams, and mobile apps.
The average data volume is growing by 63% per month, according to the survey.
However, most organizations lack the data storage capacity, computing power, and analytical capabilities to effectively manage and gain value from these big data streams.
Only 20% of data is currently being used for analytics, while the rest remains dark data that is not leveraged.
To overcome these challenges, companies need to invest in new technologies like data lakes, data warehouses, and big data platforms. They must also develop robust data governance practices to ensure data quality, security and privacy.
The Rise of AI Data Clouds
Image Source: Salesforce, Snowflake
In recent past, a new generation of more efficient data cloud platforms emerged to help organizations better manage and derive value from their rapidly growing volumes of unstructured data and big data.
Key features that have driven the rise of data clouds include:
Scalable storage and compute
Data clouds can elastically scale storage and processing power to handle petabytes of data and complex queries, without the need to manage underlying infrastructure.
Support for structured and unstructured data
Data clouds provide native support for storing and querying a wide variety of data formats, from relational tables to JSON, Parquet, and Avro files.
Integrated analytics
Data clouds come with built-in capabilities for data preparation, BI, machine learning, and real-time analytics, reducing the need for separate tools.
How Orgs Can Benefit from Data Clouds
|
Industry |
Use Case |
Examples |
|
Finance |
Unified Customer Profiles |
Integrate customer, account, and transaction data for better client services. |
|
Healthcare |
Improved Patient Care |
Optimize clinical trials and enhance patient interactions. |
|
Retail |
Personalized Shopping Experiences |
Offer dynamic pricing and personalized recommendations. |
|
Media and Communications |
Enhanced Content Recommendations |
Personalized content delivery and customized subscriptions. |
|
Transportation |
Fleet Management and Traffic Analysis |
Optimize fleet management and improve route planning. |
|
Software Development |
Test and Development Environments |
Speed up app and software creation. |
Salesforce Data Cloud vs Snowflake Data Cloud
| Feature | Salesforce Data Cloud | Snowflake Data Cloud |
| Purpose | Customer Data Platform (CDP) for unified customer profiles and real-time engagement | General-purpose data platform for diverse data types and workloads |
| Data Integration | Integrates with Salesforce ecosystem; includes connectors for Snowflake, enabling bi-directional data sharing | Integrates with various data sources and platforms, supports ETL, BI, and other apps |
| Real-Time Capabilities | Supports real-time data streams and zero-copy data sharing with Snowflake | Real-time data processing and analytics, designed for high performance |
| Data Management | Combines first-party data for marketing, sales, and service activities; limited in data transformation capabilities | Handles a wide variety of data types including structured and semi-structured data; extensive data transformation capabilities |
| Scalability | Scalable within the Salesforce ecosystem, but primarily focused on customer data | Highly scalable, supports large-scale data warehousing and processing |
| Security & Compliance | HIPAA, ISO, and GDPR compliant; integrated security features within Salesforce ecosystem | Comprehensive security features including SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI DSS compliance; role-based access control |
| Pricing Model | Primarily sales, marketing, and service teams within organizations using Salesforce | Database engineers, data analysts, and business intelligence professionals |
| Customer Support | Email and phone support; support tickets through Salesforce | Email, phone, and live support; detailed support tiers |
| Key Differentiators | Seamless integration with Salesforce CRM; real-time customer insights and actions | Broad data handling capabilities; high-performance analytics; advanced security and compliance features |
| Notable Features | – Zero-copy data sharing with Snowflake – Real-time customer profile updates – Integrated AI with Einstein | – Support for multiple data formats (Avro, JSON, Parquet, XML) – Multi-cluster warehouse – Zero-copy cloning |
We have a detailed guide about Salesforce Data Cloud. You can check it here.